Effective chatbot design isn’t just about code; it’s the strategic process of planning and refining an automated conversation that aligns with a specific business goal. A well-built AI chatbot requires understanding your user’s mindset, structuring the flow, shaping the dialogue, and ensuring the chatbot UI and UX feel seamless. It also means preparing a backup plan for when the AI agent doesn’t understand or when the user moves off-track.
A great design transforms a simple question-and-answer tool into a powerful extension of your interface, driving marketing, sales, or customer support operations. Let’s break down how to get there and what it really takes to design a high-performing chatbot.
Laying the Groundwork for an Effective Chatbot Design
Before writing a single line of dialogue, you need a solid strategy. This foundational step separates a genuinely helpful AI agent from a frustrating dead end. When the planning is done right, the bot feels intuitive—its UX guides users exactly where they need to go, with minimal friction and a clear, user-friendly interface.
While today’s AI-powered systems feel cutting-edge, the idea of conversational machines has deeper roots. It started in 1966 when MIT’s Joseph Weizenbaum created ELIZA, a chatbot that mimicked a psychotherapist. ELIZA used simple pattern matching to mirror a user’s language, creating a surprisingly human-like interaction for its time. That early system laid the groundwork for the AI chatbots and intelligent interfaces we design today. You can read more about the history of chatbot technology on Kore.ai.
Nail Down Your Primary Business Goal
What is the single most important job this chatbot needs to do? Trying to build a bot that does everything is a guaranteed recipe for a clunky, confusing experience. Instead, get laser-focused on a clear, measurable objective that delivers immediate value.
A focused goal makes every other design decision—from the tone of voice to the conversation paths—a hundred times easier.
For example, is your bot’s main purpose to:
- Qualify marketing leads by asking targeted questions and capturing contact info?
- Provide 24/7 customer support by instantly answering common questions about shipping or returns?
- Drive sales by offering personalized product recommendations and discount codes?
- Streamline appointment bookings by integrating directly with your calendar?
A chatbot with a singular, well-defined purpose will always outperform a jack-of-all-trades. If your goal is to reduce support tickets by 20%, then every feature and line of dialogue must serve that specific mission.
Create Simple User Personas
You can’t design a great conversation without knowing who you’re talking to. User personas help you lock in on your audience’s needs, motivations, and potential frustrations. This step ensures your bot’s personality and language connect with real people.
This visual shows how the strategy flows: goals inform personas, which then shape the user journey. These are the pillars of effective chat bot design.
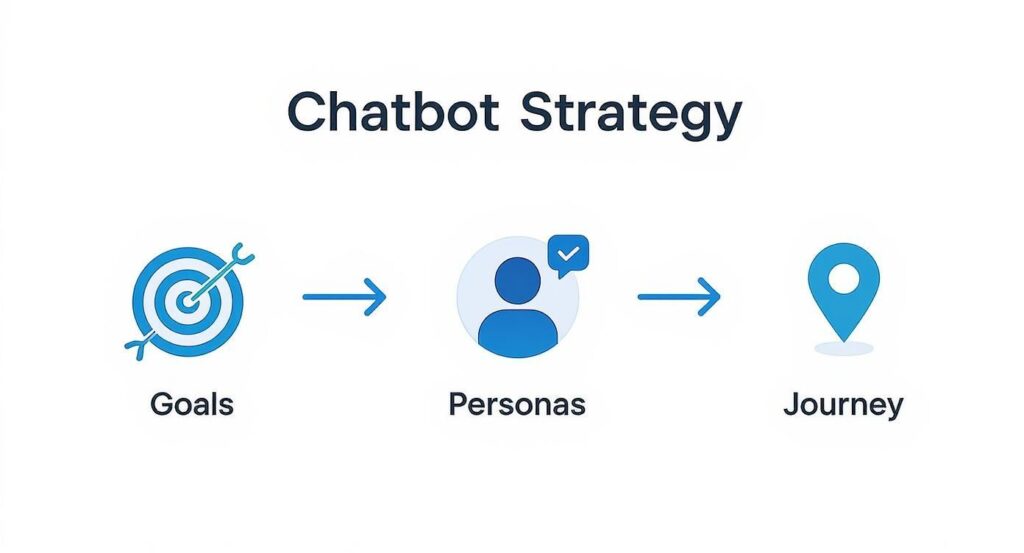
Chatbot Strategy Flow
This process ensures your bot is built on a foundation of real user needs and clear business objectives. When you’re laying this groundwork, it’s also helpful to understand the role of AI in business automation to see the bigger picture.
Consider creating personas like these:
- “Busy Brian”: A returning customer who knows what he wants. He values speed and efficiency. For Brian, the bot should offer quick links and cut the small talk.
- “Curious Carol”: A new visitor exploring your products. She needs guidance and recommendations. For Carol, the bot should be proactive, friendly, and ready to help her discover options.
Understanding these different user types allows you to build a flexible conversation that caters to multiple needs without feeling generic.
Defining these core elements upfront is non-negotiable. This table breaks down what you need to figure out before you start building.
Core Components of Chatbot Strategic Planning
| Strategic Element | Key Question to Answer | Example for a Sales Bot | Example for a Support Bot |
|---|---|---|---|
| Primary Goal | What is the single most important outcome? | Increase qualified leads by 15% in the next quarter. | Reduce support ticket response time by 30%. |
| Key Metric | How will we measure success? | Number of leads with valid contact info collected. | Number of successfully resolved issues without human agent. |
| Target User Persona | Who are we talking to? | “Curious Carol,” a first-time visitor needing product guidance. | “Busy Brian,” a returning customer with a specific order question. |
| Main Use Case | What is the bot’s primary function? | Offer personalized product recommendations and a discount. | Answer FAQs about order status, shipping, and returns. |
| Brand Voice | What personality should the bot have? | Friendly, enthusiastic, and helpful personal shopper. | Calm, efficient, and professional problem-solver. |
With these strategic pieces in place, you’re ready to move from planning to actual design, confident that your bot is set up for success from day one.
Crafting Conversations That Actually Connect
With your strategy locked in, it’s time for the fun part: scripting dialogue and designing a user experience that doesn’t feel robotic. This is where your chatbot idea starts to feel like a genuine conversation partner.
The goal is to build flows so intuitive that users never feel lost or stuck in a loop. A great conversation starts with a great first impression. That first message must build rapport, set expectations, and instantly show the user what’s possible. A vague “How can I help you?” is a dead end waiting to happen.
Designing Intuitive Conversation Flows
Think of a conversation flow as a user’s roadmap. Every turn should feel logical, and the destination should always be clear. The best chat bot designs guide users effortlessly with a mix of clear prompts, helpful shortcuts, and anticipating their next move.
Here’s how to make your flows feel effortless:
- Use Quick Replies and Buttons: Don’t force users to type everything. Offer buttons like “Track my order” or “See top sellers” to make navigation fast and foolproof. This one change dramatically cuts down on user effort.
- Set Expectations Immediately: Start with a clear introduction. For example: “Hey! I’m the [Brand] virtual assistant. I can help you track orders, browse products, or connect you with a team member. What would you like to do?”
- Keep Responses Short and Scannable: No one wants to read an essay from a bot. Break your messages into small, digestible chunks. Well-placed emojis can also add personality and make the text easier to read.
The core of effective chat bot design is minimizing cognitive load. The less the user has to think, the better the experience. Guide them, don’t just quiz them.
Giving Your Bot a Distinct Personality
A chatbot without a personality is just a sterile Q&A machine. To build trust, your bot needs a consistent voice that reflects your brand. Is it witty and fun? Or professional and straight-to-the-point?
Nailing this down early makes writing every line of dialogue easier. A consistent personality makes the user feel like they’re talking to a single entity, building familiarity and trust. You can find excellent pointers in our guide on effective chatbot copywriting.
Writing Dialogue That Feels Natural
The secret to dialogue that connects is to write like a human talks. Ditch the corporate jargon and stiff, formal language. Your goal is a script that feels natural, helpful, and even a little empathetic.
For example, instead of saying, “Your query has been received and will be processed,” try something warmer like, “Got it! Let me look that up for you.” That small shift in tone makes a world of difference.
Here are a few practical tips for writing better bot dialogue:
- Use Contractions: “You’re” and “it’s” sound far more natural than “you are” and “it is.” It’s a simple change that makes the conversation feel less stilted.
- Vary Your Greetings and Responses: Don’t use the same “Hello” or “Okay” every time. Program a few variations to make the conversation feel more dynamic and less repetitive.
- Acknowledge User Input: Simple phrases like “Great choice!” or “I can definitely help with that” confirm that the bot understood the request and is taking action.
By focusing on intuitive flows, a clear personality, and natural dialogue, you can craft an experience that not only solves problems but also strengthens your relationship with your audience.
How to Build Your Bot Without Writing Code
Gone are the days when you needed a computer science degree to build a chatbot. Modern no-code builders have completely changed the game, turning what used to be a complex coding project into a visual, drag-and-drop process.
This means you can focus on what matters—crafting a great conversation—instead of getting lost in technical jargon. It’s about working smarter, not harder.
Understanding the Visual Flow Builder
The heart of any no-code platform is its visual flow builder. Imagine a digital whiteboard where you map out your bot’s conversation using simple blocks. Each block represents an action: sending a message, asking a question, or adding a tag to a user.
You connect these blocks to create a logical path for the user. This visual layout makes it incredibly easy to see how the conversation unfolds and spot any potential dead ends before you go live. The best way to understand this is to try a no-code chatbot builder for yourself.
This is what a typical flow looks like. The connected blocks guide the user’s entire journey.
Typical Chatbot Design
Each element is a step in the conversation, making it simple to design and troubleshoot even complex interactions.
A Practical Example: Lead Qualification Flow
Let’s walk through a real-world scenario: building a lead qualification bot for a marketing agency. The goal is to automatically identify high-value prospects and get them to book a demo.
Here’s how you could map it out in a no-code builder:
- Start with a Hook: The bot opens with a friendly message: “Hey! Looking to boost your marketing ROI? We can help. Are you interested in a free strategy session?” It then offers two buttons: “Yes, tell me more!” and “No thanks.”
- Ask a Qualifying Question: When a user clicks “Yes,” the bot digs deeper: “Great! To make sure we’re a good fit, what’s your current monthly ad spend?” It provides pre-set options like “<$1k,” “$1k-$5k,” and “>$5k” to keep it simple.
- Use Conditional Logic: Here’s the magic. If someone selects “>$5k”, the bot instantly knows they’re a high-value prospect and tags them. It then pivots the conversation: “Perfect, it sounds like our Pro plan would be a great fit. Let’s get you on a quick demo with our team. What’s the best email to send the calendar link to?”
- Capture the Lead & Integrate: Once the user provides their email, an integration block automatically sends that contact info straight to your CRM, like HubSpot or Salesforce.
- Schedule the Meeting: To close the loop, the bot sends a direct link to a Calendly or SavvyCal page. The lead books a demo on the spot. Just like that, a qualified meeting is on your sales team’s calendar.
You can build this entire automated flow in under an hour without writing a single line of code. You’ve just transformed a passive website visit into a 24/7 lead generation machine.
This framework isn’t just for agencies. An e-commerce store could use it to recommend products based on a quiz. A consultant could use it to pre-screen new clients. The key is to break your goal into a series of simple, logical steps and use the visual builder to bring it to life.
Planning for When Things Go Wrong
Even the best-designed bots get tripped up. What separates a great chatbot from a frustrating one is how it handles those moments of confusion. Planning for errors isn’t a weakness in your design; it’s a critical feature that builds trust and keeps conversations from hitting a dead end.
No one wants to see a generic “I don’t understand” message over and over. A smarter approach is to design helpful fallbacks that gently steer the conversation back on track.
Chatbot Design API Workflow
This process—gracefully handling the unexpected—is what makes a bot feel truly robust. Let’s look at how to build bulletproof fallback strategies and create a seamless handoff to a human when needed.
Designing Helpful Error Messages
A good fallback message does more than admit confusion; it offers a solution. The goal is to “fall forward” by guiding the user toward a successful outcome.
Here’s a simple framework for better error messages:
- Acknowledge the Issue: Start with a human-sounding phrase like, “Hmm, I’m not quite sure I follow.”
- Suggest Alternatives: Offer quick-reply buttons based on what you think the user might be trying to do. If someone types “cancel my thing,” your bot could offer buttons for “Cancel Order” and “Cancel Subscription.”
- Provide an Escape Hatch: Always include an option like “Talk to a person” or “See Main Menu.” It’s a non-negotiable safety net.
This approach transforms a potential dead end into a helpful detour, keeping the user engaged and in control.
Knowing When to Escalate to a Human
Automation is powerful, but it can’t solve everything. A core part of smart chatbot design is knowing the exact moment to get a human involved. A smooth handoff is critical for handling complex, high-value, or emotionally charged situations.
Don’t think of a human handoff as a failure. See it as the successful completion of the bot’s real job: triaging the request and getting it to the right resource efficiently.
Set up specific triggers that automatically escalate a conversation to your live support team. These triggers are your system’s safety net.
When designing your escalation logic, it’s crucial to compare different strategies for handling errors and handoffs.
Effective Fallback and Escalation Strategies
| Scenario | Poor Strategy (Avoid This) | Effective Strategy (Implement This) |
|---|---|---|
| Repeated Misunderstanding | The bot repeats “I don’t understand” three times. | After two failed attempts, the bot says, “I’m having trouble. Would you like to connect with a human agent?” |
| Negative User Sentiment | The bot ignores words like “frustrated” or “angry.” | The bot detects negative sentiment and proactively offers to escalate to a live agent. |
| High-Value Sales Inquiry | A user asking about “enterprise plans” gets a link to the pricing page. | The bot identifies the high-value intent and immediately routes the chat to the sales team for a live takeover. |
| Direct Request for Help | A user types “talk to a person,” and the bot replies with menu options. | The bot instantly recognizes the request and initiates the handoff process without further questions. |
These strategies make the difference between a user who feels heard and one who feels trapped in a loop.
Common triggers to build into your bot include:
- High User Frustration: The bot can detect negative sentiment from words like “useless” or “annoyed.” You can also trigger an escalation if a user hits the same fallback message two or three times in a row.
- High-Value Intent: If a user mentions enterprise pricing or bulk discounts, that’s a conversation you want a skilled sales rep handling immediately.
- Explicit Request: When a user asks for a “live agent” or to “talk to a human,” the bot’s only job is to make that happen fast.
When the handoff occurs, the bot must pass the entire conversation history to the agent. This gives your team the full context needed to solve the problem without forcing the customer to repeat themselves—a massive win for customer satisfaction.
How to Test and Optimize Your Chatbot
Launching your chatbot isn’t the finish line; it’s the starting gun. The continuous cycle of testing and data-driven optimization is what separates a decent bot from an indispensable business tool.
This process must start long before your bot chats with a real customer. Internal testing is your chance to catch awkward phrasing, broken conversation paths, and dead ends before they can damage your brand’s reputation.
Practical Quality Assurance Techniques
Before you go live, you need to put your chatbot through its paces. The goal is to simulate how real people will interact with it and uncover every potential point of failure. Don’t just test the “happy path” where a user does everything perfectly. Actively try to break it.
Here are a few essential QA tests you must run:
- Keyword Variations: Test synonyms, slang, and common misspellings. If your bot handles “shipping status,” see what happens with “where’s my stuff,” “delivery update,” and “track package.”
- Conversation Hijacking: See what happens when a user abruptly changes the topic. If the bot is qualifying a lead and the user suddenly asks about pricing, does it handle the pivot gracefully or collapse?
- Boundary Testing: What happens when someone types an unusually long sentence? A single word? Or just an emoji? A well-designed bot should handle these edge cases without crashing.
The most insightful feedback often comes from trying to confuse your bot on purpose. If you can’t break it, you’ve built something solid. If you can, you’ve found a critical area to fix before your customers do.
Measuring What Truly Matters
Once your bot is live, the focus shifts to performance data. Vanity metrics like “total conversations” won’t tell you much. You need to track the key performance indicators (KPIs) that tie directly back to your business goals.
The right metrics give you a clear, unbiased look at what’s working and what isn’t. You can get a deep dive by exploring these essential chatbot KPI metrics and how to track them.
At a high level, here are the key metrics to monitor:
- Goal Completion Rate (GCR): This is the ultimate measure of success. What percentage of users actually accomplish their goal, whether it’s booking a demo or resolving a support ticket?
- Fallback Rate (FBR): How often does your bot have to say, “Sorry, I don’t understand”? A high fallback rate is a massive red flag that your bot needs better training or is missing key conversation paths.
- User Satisfaction (CSAT): Nothing beats direct feedback. A simple thumbs-up/thumbs-down at the end of a chat gives you an immediate pulse on the user experience.
Turning Insights into Action
Data is useless if you don’t act on it. The final step in creating a chatbot that truly performs is to regularly analyze your metrics and conversation logs to uncover improvement opportunities. This is a continuous optimization cycle that sits at the core of good chatbot design: measure, learn, refine.
For example, comb through your “unanswered questions” log. If multiple users ask the same question your bot can’t handle, that’s a clear signal to build a new conversation flow or update the chatbot interface to better guide them. These insights form the foundation of strong AI design and ensure your system evolves intelligently.
Similarly, if you see a high drop-off rate at a specific point in the flow, revisit the bot’s messaging or UX at that moment. Perhaps the prompt is confusing, poorly structured, or asking for too much information at once. This is where chatbot UI design and clear conversational structure intersect. Even platforms like ChatGPT rely on this iterative feedback loop to improve user experience.
By creating this cycle—testing, measuring, and optimizing—you ensure your artificial intelligence system becomes more accurate, relevant, and impactful over time. This is what separates basic automation from truly effective conversational AI.
Your Chatbot Needs to Adapt to Its Environment
A chatbot isn’t a one-size-fits-all tool. The proactive sales AI agent that works beautifully on your website may feel intrusive or awkward inside an Instagram DM. To build a bot people genuinely want to interact with, your strategy must adapt to each environment.
Designing with the channel in mind means aligning the chatbot UI and tone with user expectations. Someone browsing your website is in a different mindset than someone casually scrolling through Messenger. Effective chatbot design respects that difference.
Website Bots: Master the Proactive Welcome
On your website, you have the home-field advantage. This is where you can use chatbot design best practices to proactively engage visitors at exactly the right moment. Don’t wait for someone to click the chat icon—bring the conversation to them through intelligent triggers.
Here are a couple of proven triggers inspired by chatbot UI examples from top-performing brands:
• Time on Page: If someone lingers on your pricing page for more than 30 seconds, trigger a helpful message:
“Hey, have any questions about our plans? I can help you find the perfect fit.”
• Exit Intent: When a visitor’s cursor moves toward the close button on the checkout page, trigger a timely message—or even a last-minute discount code. This small change can recover countless abandoned carts.
This approach transforms your system from a passive FAQ machine into an active, intelligent sales assistant—one of the best examples of how chatbot interface strategy can drive measurable results.
Messenger and Instagram: Think Visually
Social channels demand a different style. Users on these platforms respond better to visual elements, quick taps, and lightweight conversation. The chatbot UI here should be image-first, fast, and simple. Platforms like Messenger and Instagram are all about visual, informal chats. Walls of text feel clunky here. Your chat bot design needs to lean into rich media features to create a more dynamic experience.
Make the conversation feel like a natural part of the social media experience. Use carousels to let users swipe through products, quick replies to guide them through a quiz, and images to confirm their choices. It cuts down on typing and keeps things fast and fun.
Instead of just listing product names, send a scrollable product carousel. Instead of making someone type “Yes,” offer colorful quick-reply buttons. These small shifts make the interaction feel less like a form and more like a modern app.
WhatsApp: Keep It Personal and to the Point
WhatsApp is a different beast. It’s a more personal and direct channel. People on WhatsApp expect concise, high-value communication, not marketing blasts. Your design must play by WhatsApp’s rules, which often means starting conversations with pre-approved template messages.
Once a user replies, a 24-hour window opens for more free-form conversation. The tone here should be direct and helpful. This is the perfect place for a bot to handle order confirmations, send appointment reminders, or provide quick support updates—interactions that deliver immediate value to their phone.
Privacy and Trust: The Foundation for Every Channel
It doesn’t matter what channel you’re on; being upfront about data is non-negotiable, especially with regulations like GDPR. The best way to build trust is to address privacy directly within the conversation.
- Before asking for an email, have the bot say something clear: “To send your discount code, I’ll need your email. We’ll only use it for this offer and our weekly newsletter, which you can opt out of anytime.”
- Make your policies easy to find. A “Privacy Policy” button in your bot’s main menu is a simple way to build trust.
This kind of transparency shows you respect your users and their data, which is fundamental to building any long-term customer relationship.
Got Questions About Chatbot Design? We’ve Got Answers.
Even with a solid plan, questions will come up. Here are straight, practical answers to some of the most common challenges in designing a chatbot.
Don’t Pretend Your Bot Is Human
One of the biggest mistakes in chatbot UX design is trying to trick users into believing they’re speaking with a person. It sets unrealistic expectations and leads to frustration when the bot inevitably hits a limitation.
Instead, set the right tone upfront with a clear intro like:
“Hi, I’m the automated assistant for [Your Brand].”
This transparency builds trust and ensures your bot is judged on what it’s designed to do—not what users imagine it can do.
Focus on making the bot excellent at a few specific tasks rather than attempting to mimic human conversation perfectly. A reliable, purpose-built bot always outperforms a generic one that overpromises and under-delivers.
Conclusion
Effective chat bot design relies on strong design principles and a clear chatbot design process that bridges conversation design, visual design, and user interface considerations to create a user-friendly chatbot and a positive user experience. Whether you start with a rule-based or complex chatbot powered by large language models (llm) and AI algorithms, focusing on chatbot best practices, design patterns, and training the chatbot ensures the chatbot provides relevant, context-aware responses and a consistent chatbot personality; this makes interacting with a chatbot feel natural across a mobile app, Facebook messenger and website chatbot design, or large desktop environment.
Practically, use UI elements, GIFs, avatars, and CSS to craft a chatbot conversation that users interact with your bot willingly. While integrating live chat or a platform for cross-app AI actions when escalation is needed. The chatbot uses analytics to refine workflows to be context-aware, so many chatbot interactions remain relevant to user needs.
Ready to build a chatbot that delivers real results? With Clepher, you get an intuitive, no-code builder to design, launch, and optimize powerful AI chatbots for your website, Messenger, Instagram, and WhatsApp. Start turning conversations into conversions today.
Related Posts